What Is EDI? And Can It Really Ease Business Communications?
 James Smith
James Smith
Table of contents
Data exchange is an integral part of any business between vendors, suppliers, logistics, and several other business partners. Without an automated system in place, you need resources to manage data manually which is time-consuming and not cost-effective. There are also concerns about processing time, manual errors in the transmission of data, unorganized or scattered data without a singular dashboard to analyze and review – which can cause severe setbacks to your business.
Chances are that some of your partners or vendors already have an Electronic Data Interchange or EDI software in place. This means that while your vendors and partners can share and analyze data in real-time, they must, however, bear with delays and even errors from your end. This will eventually affect your bottom line and reduce customer satisfaction. In absence of an automated process, the need for manual error detection becomes necessary which is an added cost for your business. Add to that list, is the difficulty of tracking security concerns of the data exchanged between your business and other partners.
If you are looking to scale your business but are being held back due to the lack of an automated data integration technology in place, EDI might just be the right technology for you. In this beginner’s guide to EDI, we will cover the following topics:
History and evolution of EDI
Although an electronic method of communication only took off in the 60s, railroads used telegraphs to send out messages using Morse Code way earlier in the 1850s. The birth of the technology can be attributed to the need for streamlining communication for the U.S. transportation industry in the 1960s. The objective was to create an accurate and standardized format to share documents such as orders, invoices, etc., between multiple computer systems.
In 1979, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) created a committee (Accredited Standards Committee or ASC) to regulate EDI. With the boom of industrialization and the growth of multinational organizations, the need for EDI spread across the globe. And by 2001, the ASC and the UN/EDIFACT Working Group (EWG) released a global standard for EDI. Fast track to 2021, and several more industries have adopted EDI, with over 150,000 companies worldwide using various standard formats based on industry and region.
What is EDI?
There are several definitions of EDI one might find. But, to put it plainly, EDI is the electronic exchange of essential documents (also referred to as messages) between businesses using a standardized format. Therefore, it replaces the practice of sending out paper-based documents that were earlier sent out by post, fax, and/or email. The use of EDI streamlines the communication process with the use of a standardized format.
One of the older definitions of EDI by the National Institute of Standards and Technology still stands true – "the computer-to-computer interchange of strictly formatted messages that represent documents. EDI implies a sequence of messages between two parties, either of whom may serve as originator or recipient.”
It is important to note that this exchange of important information between computers in a standardized format can occur not only between two business partners but also within an organization. Therefore, EDI facilitates the process of businesses communicating vital information using structured data, and agreed-upon message standards, from one computer system to another.
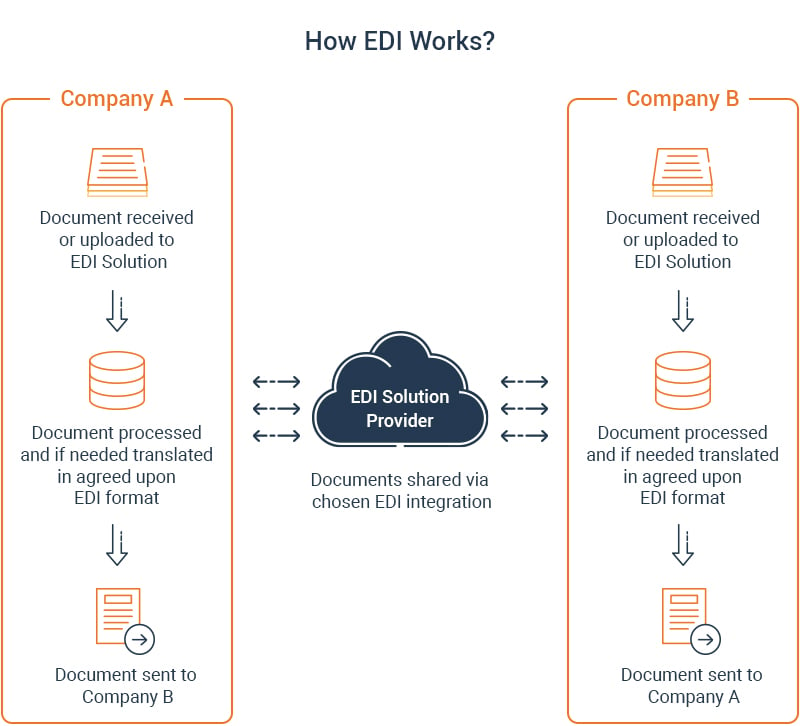
Which documents can be shared via EDI?
Today, industries use EDI integration to share a range of document types. The most common document flow exchanged between business partners’ computer systems are purchase orders, invoices, and advance ship notices. Several other documents are transmitted via various EDI formats depending on industry and region.
-
Food retail or FMCG (Fast-moving consumer goods) organization: requests for quotations, order status inquiries, product transfer, resale reports, etc.
-
An e-commerce company: booking confirmations, shipping status, customs documents, and others.
-
A manufacturer: motor carrier load tenders, requests for routing instructions, product activity data, advance ship notices/manifests, etc.
-
A healthcare/medicare organization: application advice, price information, functional acknowledgments, and so on.
-
A supplier: credit/debit adjustments, consolidated service invoice statements, sales catalogs, and other documents.
-
Logistics companies: reservation bookings, status details, warehouse shipping orders, response to a load tender, and so on.
We have listed just a few formats across some of the industries where EDI is most prevalent. However, the scope is vast as more and more industries adopt EDI.
What is an EDI standard format?
We now know that EDI documents follow a standard format for smart systems to understand and transmit that data forward. A standard format sets a fixed guideline for each set necessary item of information. So, without this format, EDI technology or electronic data interchange is of no use. Therefore, companies cannot customize or change this format based on their preferences.
What we must understand is that there is a family of standard formats, as these formats vary based on industries and regions. Some of these are - X12, EDIFACT, TRADACOMS, and ebXML. Each standard might have many different versions based on the ERP they are integrated with. Before business or trading partners start the process of an EDI exchange, they have to not only agree upon an EDI standard but a version as well. The way around different versions is adding on an EDI translator that can understand and translate the EDI format in use and ease the processing of documents efficiently.
Does EDI need any human intervention?
While most solution providers might claim that EDI does not need any human intervention and that all documents are formatted, interpreted, and transmitted by computer systems, that is far from the truth. A computer system can only read data accurately if the document follows the standard formats and protocols. Once EDI has been implemented, the various checklists for each format, such as data structure, document type, etc., must be followed. There are different standardized formats for different industries. Therefore, the truth is that EDI facilitates the automated exchange of commercial messages with minimum human intervention.
Human intervention will be needed in stages of quality checks, system errors, or when sensitive data needs to be filled individually in rare cases.
Why EDI?
Sharing business documents manually via post, fax, and email was how people operated before the boom of EDI. Below are the benefits of integrating EDI with your ERP.
Improves Processing Speed
All transactions/documents are automatically shared in real time, irrespective of time zones. There is no need for the team to manually understand and feed in data which could otherwise take hours or even days.
Reduced Margin for Errors
As documents are sent out in standard and agreed-upon formats in EDI, there is a streamlined means to communicate. If companies were to send out documents in their own formats. The receiver would have to understand and then process that document based on the organization’s required format.
Convenient and Efficient
The standardization and strict formatting guidelines that come with EDI make transferring of information irrespective of language convenient and more efficient for your business and trading partners. For example, a Finnish organization is acquiring goods from a Taiwanese company. The exchange of information between both companies will be in accordance with the industry format, which means efficient and accurate document exchange, irrespective of language barriers. This situation, if handled manually, would need third-party translation services that would delay the processing of the transaction.
Cost-effective
Traditional methods of sharing information manually tend to use paper. An electronic exchange saves the cost of printing, storing, and copying documents and is also better for our environment.
Free Up Resources
Adopting an automated technology, such as EDI, frees up resources that were earlier spending large amounts of their time processing documents. They can now focus on data analysis and other important tasks to enhance business productivity.
If you are keen to tap into the advantages of EDI and would like to evaluate the type of EDI solution best suited for your business, then read our blog that explains the options available for EDI Integration based on various scenarios.
Related Reading: EDI Integration with ERP: What Are Your Choices? (Explained with Scenarios)
Is integrated EDI the right solution for your business?
Data integration and automation are a given in most industries. However, for certain businesses, the traditional ways of doing things may result in missed opportunities and even losses over time. The advantages of EDI are numerous. STAEDEAN's customers that have implemented our integrated EDI solution for Dynamics 365 F&SCM—EDI Studio, have witnessed added accuracy, efficiency, improved processing time, and reduced delivery time. In fact, EDI Studio has empowered our customers to achieve meaningful digital transformations across their businesses within their Microsoft ERP environment.
In a world moving towards remote operations and more reliance on ERP systems, it makes sense to upgrade your ERP to integrate automated processes that can streamline communications remarkably. To continue your journey of understanding EDI and overcome EDI challenges, we recommend that you download our EDI Toolkit. Our toolkit covers the implementation challenges and ways to overcome those, the scenarios you could consider, the several benefits of implementing an integrated EDI solution, among other topics that will give you insights to confidently get started on your journey to data transformation.


